buy pumice stone + introduce the production and distribution factory
The discovery of pumice stone has been a turning point in the history of skin care with its porous granular texture resulted from mixture of volcanic lava with water
Also, for its wide industrial properties that will be discussed further in the text is considered a milestone product of all times in history
Pumice is an aluminum silicate with igneous origin and cellular and porous structure
This lightweight sponge forms in erupting volcanic eruptions
Pumice or mineral pumice has a network of gas bubbles in volcanic glass and minerals
Pumice can be formed in different types of magmas such as basaltic, andesitic, dacitic and rhyolite magmas
Pumice has the same origin and chemical composition and differs from pumice only in grain size
Due to the fact that there is a lot of gas and water vapor in the composition of pumice and pumice, the specific weight of these materials is usually very low and their volume is high
(The specific gravity of pumice is often less than one)
Today, we see the use of pumice in the poultry industry and supplements and livestock and poultry feed and many other industries around the world

Pumice concrete blocks contain mostly 0
5 to 6 mm pumice in their production
The strength of this type of concrete is 2 times more than that of ordinary concrete blocks
While the weight of pumice blocks is 4 times lighter than ordinary concrete blocks
It is interesting to know that pumice concrete is also much more resistant to earthquakes
For these reasons, it is widely believed that pumice rock discovery has been a turning point in the history of skin care and industry
Pumice rock characteristics
Important features of pumice
Application of pumice stone
Main features of pumice
Major reserves of pumice in the world
Application of granulated pumice stone in industry
Pumice stone in thermal insulation
Application of pumice in chemistry
Pumice and insulation at low temperatures
Pumice and high temperature insulation
Also discussed in the text are pumice stone’s: Properties Etymology Location Mining Uses
Pumice rock characteristics
Low apparent specific gravity
Room building
Weight style
Sound and heat insulation
Excellent abrasion capability in nature
pumice is found in white, gray, pink, pale yellow or brown colors
Important features of pumice
Important features of pumice Among the important features of pumice are the following:
Agriculture and horticulture Insulation at low temperatures
High temperature insulation In the foundry industry Production of explosives
In filters Growth and propagation of plants Soil and grass improvement
Seed growth
Hydroponic culture
ceramic Building Materials
Construction parts
Ordinary plaster made Special plasters Masonry
filler insulation
Sound insulation
Bricks of Roof coverings
Floor insulation
Lightweight concrete insulation
Pipe covers of Stone facade Filler
Pumice is very abrasive and light
Today, pumice powder is yet being utilized as a superior pozzolan
Powdered pumice is used as a first-class pozzolan
Application of pumice stone
These days, the consumption of pozzolanic pumice stone has played a high role in the industry
Pumice as a silica mineral is a major stone in the construction industry
Pumice is involved in precast concrete and lightweight concrete blocks called pumice blocks
Pumice is used in various types of filtration of petrochemical oils from sugar to vegetable oils and juices
Today, we see the use of pumice in the poultry industry and supplements and livestock and poultry feed and many other industries around the world
Pumice concrete blocks contain mostly 0
5 to 6 mm pumice in their production
The strength of this type of concrete is 2 times more than that of ordinary concrete blocks
While the weight of pumice blocks is 4 times lighter than ordinary concrete blocks
It is interesting to know that pumice concrete is also much more resistant to earthquakes
pumice is also a very good insulator in terms of sound, heat and cold
Most uses of pumice are in its expanded state
Which countries have the largest pumice reserves in the world?

Before answering this question, let’s take a brief look at the features of pumice: You must know that the main feature of mineral pumice is its lightness and water resistance
It stays afloat
It is also widely used in agriculture as a mineral fertilizer
This mineral is high in silica, sulfur and phosphorus
Due to its sound and temperature insulation, it has been used as one of the most important materials in the world, but it is also one of the most popular materials in construction
Which countries have the largest pumice reserves in the world? Before answering this question, let’s take a brief look at the features of pumice:
Main features of pumice
its lightness and water resistance
It stays afloat
It is also widely used in agriculture as a mineral fertilizer
This mineral is high in silica, sulfur and phosphorus
Due to its sound and temperature insulation, it has been used as one of the most important materials in the world, but it is also one of the most popular materials in construction
Major reserves of pumice in the world: Pumice reserves in the world are limited to a limited number of countries
The largest reserves of pumice are in the United States, estimated at about 250 million tons, which may total more than 1 billion tons
According to the British Geological Survey (BGS), the global production of pumice in 2010 was about 17,300,000 tons, of which Turkey, Italy, Iran, Greece, Syria and Chile are the largest producers

Also
countries like: Algeria, Cameroon, Chile, Ecuador, Greece, Guatemala, Iran, Italy, New, Zealand, Saudi Arabia, Spain, Syria and Turkey are amongst the producers of pumice
Application of granulated pumice stone in industry: Expanded granular pumice is used in the following cases,
Preparation of lightweight concrete
Filling
Thermal and acoustic insulation
Agriculture
As a filter (filtering)
Abrasive Pumice can be mixed with cement in various proportions to make lightweight pieces
Pumice mortar is lighter than cement mortar
The thermal conductivity of the pumice is low and its absorption is higher
Pumice is also used in painting, plastics, rubber and insulating the empty space of double-walled walls
Expanded pumice is used to make various filters
Pumice is also used to separate bacteria and algae in water treatment plants
These filters are used to refine fruit juices, syrups and sugar factories
Pumice stone in thermal insulation
They are used as good thermal and acoustic insulators
Sound absorbing plates are made of a mixture of pressed pumice and asbestos
Pumice is widely used to insulate tanks and pipes up to 1000 ° C
After crushing and granulation based on its physical properties, it has various applications such as the following:
Casting
Abrasive in soap
wax
Detergent
Decorative stones
Cover golf equipment
Application of pumice in chemistry: In chemistry, pumice is a source of silica for reacting with lime and producing calcium-silicate insulators
Pumice coagulates slag
Pumice is a silica cleaner from hydrofluoric acid
To answer the main question in the article called what is pumice and the use of pumice stone, we go to one of the most common uses of pumice
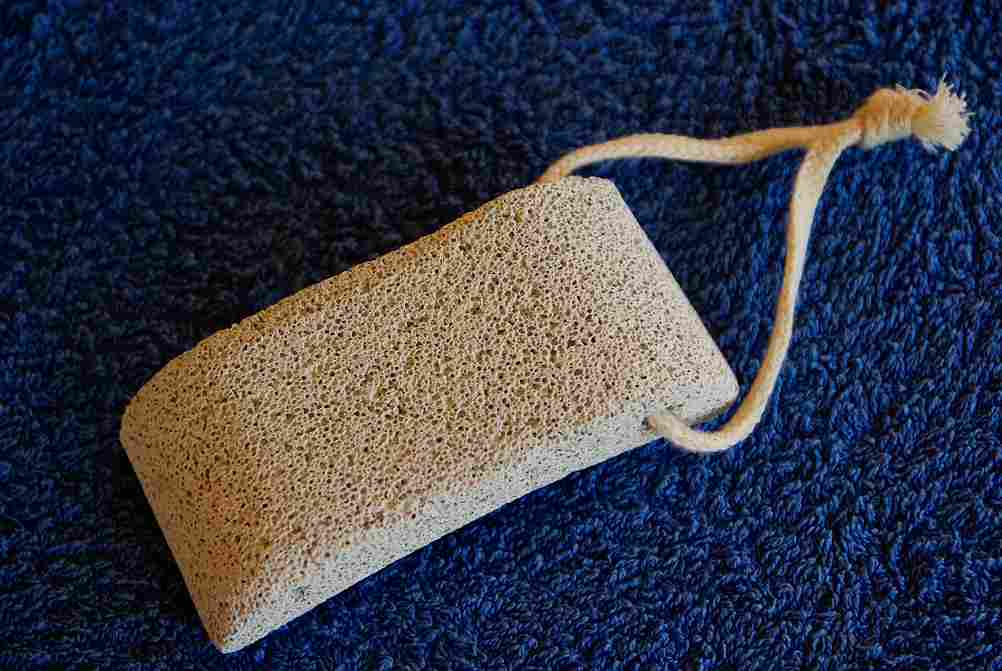

Pumice has various uses in industry due to its various properties
Most of these properties are mentioned in the construction and horticulture section
Compared to vermiculite, pumice is not a moisturizer
While being able to keep water and food at a constant level
this property makes it used in cold insulation
The harmful nature of expanded pumice and its precise processing has created enough empty spaces in it, which leads to its use in filtration processes
Pumice and insulation at low temperatures
The most important application of pumice at very low temperatures is its use in insulation and maintenance of tanks
Transportable tanks such as tankers are for storing liquid oxygen, nitrogen, argon, natural gas and other industrial gases that are stored in liquid form
The temperature of these liquefied gases varies from -33 ° C for ammonia to -269 ° C for helium
Therefore, the range of application of pumice in insulation will be at temperatures below zero degrees to -270 degrees Celsius
In low temperature applications, pumice is also used in air distillation to produce oxygen, nitrogen and rare gases
pumice is also used to fill the layer between the outside wall and inside liquid storage tanks or production towers
The advantage of pumice over other insulators is that it can be reused after changing the tank
Plastic foams are more commonly used in European countries, but pumice still has many applications in low temperature insulation
Pumice and high temperature insulation
Pumice insulation is used in steel and casting industries such as slag
In molten material that spills quickly from the pots or in molten molds
Pumice is also used in casting sand as a CUSHION agent
Mineral pumice is used in the manufacture of refractory parts and bricks
In the application of pozzolanic pumice, it can also be mentioned that expanded or raw granulated pumice is poured into pots and poured on molten metal surfaces
Pumice, due to its refractory properties that can withstand up to 1100 ° C
Pumice, also named pumicite in powdered or dust form, is a volcanic stone that consists of largely vesicular rough-textured volcanic glass, which might or might not contain crystals
It is usually light-colored

Scoria is another vesicular volcanic stone that varies from pumice in having larger vesicles, thicker vesicle walls, and being dark in color and a bit denser
Pumice is formed when super-heated, highly pressurized rock is harshly ejected from a volcano
The unusual frothy configuration of pumice occurs because of simultaneous quick cooling and rapid depressurization
The depressurization makes bubbles by decreasing the solubility of gases (including water and CO2) that are dissolved in the magma, causing the gases to suddenly exsolve (like the bubbles of CO2 that emerge when a carbonated drink is opened)
The contemporary cooling and depressurization freeze the bubbles in a matrix form
Eruptions under water are quickly cooled and the large amount of pumice created could be a shipping hazard for cargo ships
Properties
Pumice is composed of highly microvesicular glass pyroclastic with thin, translucent bubble walls of extrusive igneous rock
It is a common but not exclusive form of silicic or felsic to intermediate in composition (e
g
, rhyolitic, dacitic, andesite and pantellerite, phonolite, trachyte), but basaltic and other compositions are known
Pumice is commonly pale in color, ranging from white, cream, blue or grey, to green-brown or black
It forms when volcanic gases exsolving from viscous magma form bubbles that remain in the viscous magma as it cools to glass
Pumice is a common product related to explosive eruptions (plinian and ignimbrite-forming) and commonly forms zones in upper parts of silicic lavas
Pumice has a porosity of 64–85% by volume and it floats on water, possibly for years, until it finally becomes waterlogged and sinks
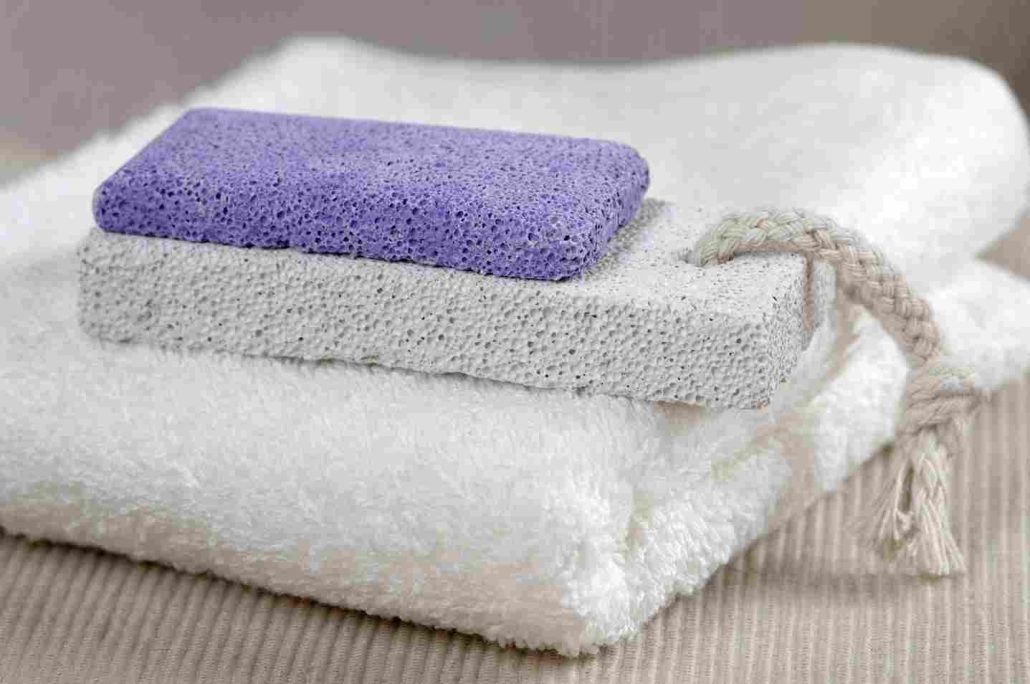
Scoria differs from pumice in being denser
With larger vesicles and thicker vesicle walls, scoria sinks quickly
The difference is the result of the lower viscosity of the magma that forms scoria

When larger amounts of gas are present, the result is a finer-grained variety of pumice known as pumicite
Pumicite is composed of particles less than 4mm in size
Pumice is considered a volcanic glass since it has no crystal structure
Pumice varies in density based on the thickness of the solid material amongst the bubbles; many samples float in water
After the explosion of mount Krakatoa in Indonesia, rafts of pumice drifted through the Indian Ocean for up to 20 years high, with tree trunks floating among them
In fact, pumice rafts disperse and support numerous marine species
In 1979, 1984 and 2006, underwater volcanic eruptions near Tonga caused large pumice rafts that floated hundreds of kilometers to Fiji
There are two major forms of vesicles
Most pumice contains tubular macrovesicles that can create a silky or fibrous fabric
The elongation of the macrovesicles happens due to ductile elongation in the volcanic conduit or, in the case related to pumices lavas, during flow
The other form of vesicles are classified as sub spherical to spherical and result from high vapor pressure during an eruption
Etymology
Pumice is an igneous rock having a foamy appearance
The name is from the Latin word Pumex (meaning “pumice”) which relates to the Latin word Spuma meaning “foam”
Long ago, pumice was called “Spuma Maris”, meaning “froth of the sea” in Latin because the frothy material was considered to be hardened sea foam
Around 80 B
C
, it was called “lapis Spongiae” in Latin language for its vesicular properties specifying it from other counterparts
Many Greek scholars decided there were different sources originating pumice, one of which was in the sea coral category
Location
Pumice can be found all around the globe forming from continental volcanic eruptions and submarine volcanic events
Floating stones can also be spread by ocean currents
As described earlier pumice is produced by the eruption of active volcanoes under certain conditions, therefore, natural sources happen in volcanically active areas
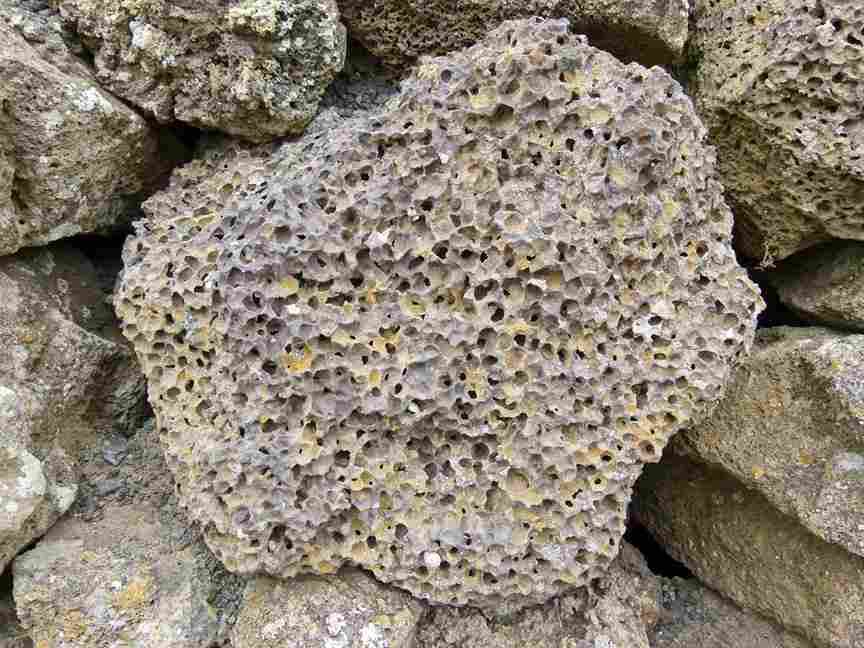

Pumice is mined and later transported from these regions
In 2011, Italy and Turkey pioneered pumice mining production at 4 and 3 million tons respectively; other large producers exceeding a million tons were Greece, Iran, Chile, and Syria
Total world pumice production in 2011 around the globe was estimated at 17 million tons
Asia
There are large reserves containing pumice in Asian countries including Afghanistan, Indonesia, Japan, Syria, Iran, and eastern Russia, each with specific features
Considerable amounts of pumice can be extracted at the Kamchatka Peninsula on the eastern part of Russia
This area has 19 active volcanoes and it lies near the Pacific belt of volcano
Asia is also the site for the second-most dangerous volcanic eruption occurring in the 20th century, Mount Pinatubo, which erupted June 12, 1991 in the Philippines
Ash and pumice lapilli were distributed over a mile away from the volcano
These ejections occupied trenches that once reached 660 feet of depth
So much magma was displaced from the vent that the volcano turned into a depression on the surface of the Earth
Another well-known volcano that widely produces pumice is Krakatoa
An eruption of Krakatoa in 1883 ejected so much pumice in the air that kilometers of sea were covered in floating pumice smoke and in some areas rose 1
5 meters above sea level
Europe Europe is the biggest producer of pumice in the world with deposits in Italy, Turkey, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, and Germany
Italy is the largest producer of pumice because it has numerous eruptive volcanoes
Mostly in Italy, the island of Lipari in Italy is entirely made up of volcanic rock, including pumice
Large amounts of igneous rock on Lipari are because of the numerous extended durations of volcanic activity ranging from the Late Pleistocene (Tyrrhenian) to the Holocene
North America Pumice can be traced all across North America including the Caribbean Islands
In the United States, pumice is mined mostly in Nevada, Oregon, Idaho, Arizona, California, New Mexico and Kansas
United States
production of pumice and pumicite in 2011 was around 380,000 tons around the whole world, valued at $7
7 million with about 46% coming from states of Nevada and Oregon
Idaho is also known as a major producer of pumice because of the quality and lightness of the rock found in its local reserves

One of the most famous volcanoes was Mount Mazama erupting 7,700 years ago in Oregon and deposited 300 feet of pumice smoke and ash around the vent
The large amount of magma erupted there caused the structure to collapse, forming a caldera currently known as Crater Lake
South America Chile is amongst the leading producers of pumice in the globe
The Puyehue-Cordón and Caulle are two widely coalesced volcanoes in the Andes mountains that ejected ash and pumice along Chile and Argentina
A recent eruption in 2011 wreaked havoc on the region by covering all areas and water ways in ash and pumice
Africa Kenya, Ethiopia and Tanzania possess some deposits of pumice
New Zealand The Havre Seamount volcano created the largest-known deep ocean volcanic eruption ever on the Earth
The volcano erupted in July 2012 but still remained unseen until enormous pieces of pumice were traced to be floating on the Pacific Ocean
Blankets of stone reached a thickness of 5 meters which is indeed huge
Most of this floating pumice is placed on the North-West coast of New Zealand and the Polynesia islands
Mining The mining of pumice is considered an environmentally friendly process in comparison with other mining methods since the igneous rock is deposited on the surface level of the earth in loose aggregate shape
The material is largely mined by modern open-pit methods
Soils are later removed by machinery in order to gain more pure quality pumice

Scalping screens are utilized to filter impure surficial pumice related to organic soils and useless rocks
Blasting is not needed because the material is unconsolidated, hence only simple machinery is applied such as bulldozers and power shovels
Different sizes of pumice are required for special uses therefore crushers are used to gain desired grades ranging from lump, coarse, intermediate, fine, and extra fine in total
Uses
Pumice is a fairly lightweight, porous and abrasive rock and it has been utilized for centuries in the building construction and beauty industry as well as in early medical science
It is also utilized as an abrasive rock, especially used in polishes, pencil erasers, and the production stages of stone-washed jeans
Pumice was also used in the ancient book-making industry to provide parchment paper and leather bindings for books
There is a wide demand for pumice, especially for water filtration, in chemical spill containment, cement production, horticulture and increasingly for the pet industry
The extraction of pumice in environmentally sensitive regions has been under more scrutiny after such an action was paused in the U
S
state of Oregon, at Rock Mesa in the south part of the Three Sisters Wilderness
Early medicine Pumice has been utilized in the medicinal industry for up to 2000 years
Ancient Chinese medicine used ground pumice together with ground mica and fossilized bones included in teas to relax the spirit
This tea was used to cure feeling of dizziness, nausea, insomnia, and anxiety disorders
Ingestion of these pulverized stones was able to soften nodules and was later used with other herbal ingredients to heal gallbladder cancer and urinary disfunctions

In western medicine, starting in the early 18th century, pumice was ground into a sugar consistency and together with other ingredients was used to heal ulcers major on the skin and cornea
Concoctions like these were also used to assist wounds scar in a healthier way
In around 1680 it was noted by an English naturalist that pumice powder was used to develop sneezing
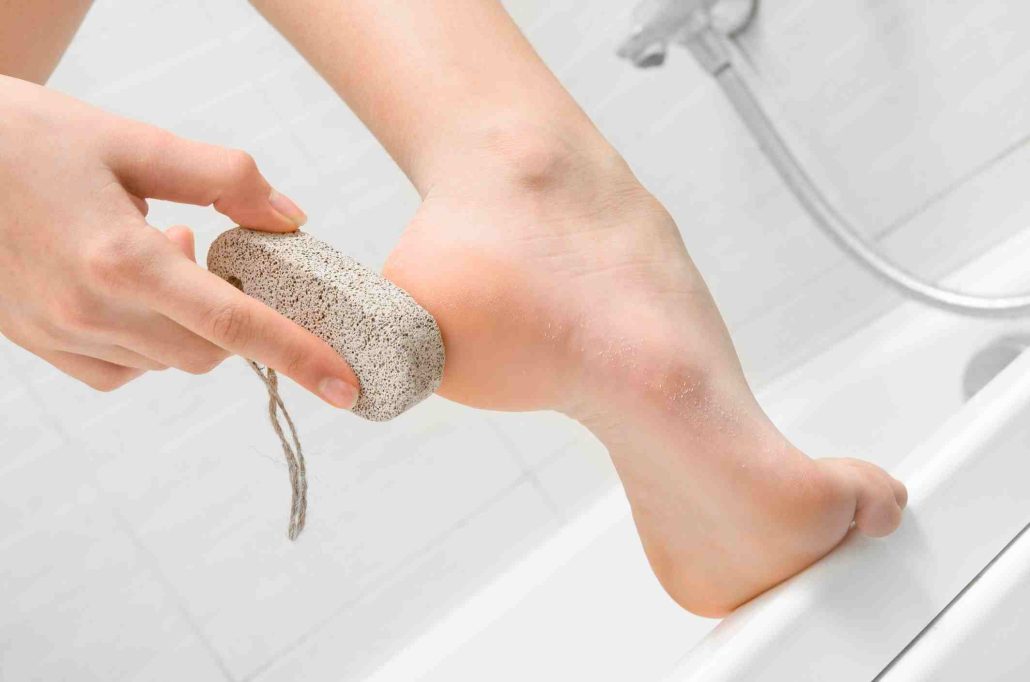
Personal care Pumice has been applied as a material in personal care for thousands of years and has a wide area of usage in medicine
It is an abrasive material that could be used in powdered form or as a medical tool to remove unwanted hair or skin
In ancient Egypt, it was widely common to remove all hair on the body to control lice and as a method of ritual purification, utilizing creams, razors, and pumice stones
Pumice in powdered version was an ingredient in toothpastes in ancient times in Rome
Nail care was highly important in ancient China; nails were protected groomed with pumice stones, and pumice stones were also rubbed on skin to remove calluses
It was founded in a Roman poem that pumice was used as a treatment to remove dead skin as far back as 100 BC, and probably before then

It has been used during many eras since then, including the Victorian Era specifically
Today, several of these techniques are yet used; pumice is widely used as a heal for skin exfoliant
Even though hair removal techniques have developed over the entire centuries, abrasive material such as pumice stones is also still used
“Pumice stones” are sometimes used in beauty salons during the pedicure process in order to remove dry and excess skin from the bottom of the feet as well as calluses
Finely ground pumice has been included in some toothpastes as a polish, like Roman use, and easily removes unused dental plaque build- up
Such toothpaste is too abrasive for every day use
Pumice is also added to heavy-duty hand washers (such as lava soap) as a fair abrasive
Some logos of chinchilla dust bath are formulated with powdered pumice in their ingredients
Old beauty techniques utilizing pumice are still used today but newer substitutes are easier to achieve
Cleaning Pumice stone, in some cases attached to a handle, is an influential scrubbing tool for removal of limescale, rust, hard water rings, or other stains on porcelain fixtures in households (e
g
, bathrooms)
It is a fast method compared to substitutes such as chemicals or vinegar and baking soda or borax
Horticulture
Good soil needs enough water and nutrient loading as well as tiny compaction to permit easy exchange of gases
The roots of plants require constant transportation of carbon dioxide and oxygen to and from the surface level
Pumice promotes the quality of soil for its porous properties, water and gases could be transported easily through the pores and nutrients can be kept in the microscopic holes
Pumice rock fragments are not organic therefore no decomposition and little compaction happen
Another benefit of this inorganic stone is that it does not absorb or host fungi or insects
Drainage is very important in horticulture, with the existence of pumice tillage is a lot easier
Pumice usage also causes ideal conditions for growing plants such as cacti and succulents as it rises the water retention in sandy soils and decreases the density of clayey soils to let more transportation of gases and water
The addition of pumice to soil develops and increases vegetative cover as the roots of plants make slopes more stable hence it helps decrease erosion

It is usually used on roadsides and ditches and mostly used in turf and golf courses to protect grass cover and flatness that could degrade due to high amounts of traffic and compaction
Regarding chemical properties pumice’s pH is neutral, it is not acidic nor alkaline
In 2011, 16% of pumice extracted in the United States was used for horticultural purposes for its wide use in this field
pumice contributes to soil fertility in regions where it is naturally present in the soil because of volcanic activity
For example, around the Jemez Mountains of New Mexico, the Ancestral Puebloans settled on “pumice patches” of the El cajole Pumice which possibly retained a bigger amount of moisture and was ideal for agriculture
Construction
Pumice is largely used to produce lightweight concrete and insulative low-density cinder blocks
The air-filled vesicles in this highly porous rock serves as a suitable insulator
A fine-grained version of pumice also called pozzolan is used as an additive in cement making and is blended with lime to form a light-weight, smooth, plaster-like concrete
This form of concrete was utilized in ancient Roman times
Roman engineers utilized it to construct the huge dome of the Pantheon with increasing amounts of pumice added to concrete for larger elevations of the structure of the dome
It was also widely used as a construction material for several aqueducts
One of the major uses of pumice presently in the United States is manufacturing concrete
This rock has been utilized in concrete mixtures for many years and continues to be used in manufacturing concrete, especially in regions close to where this volcanic material usually deposits
New studies prove a wider use of pumice powder in the concrete industry
Pumice can act as a cementitious ingredient in concrete and researchers have found that concrete made with up to 50% pumice powder can largely improve durability and reduce greenhouse gas emissions and fossil fuel consumption in various industrial machinery
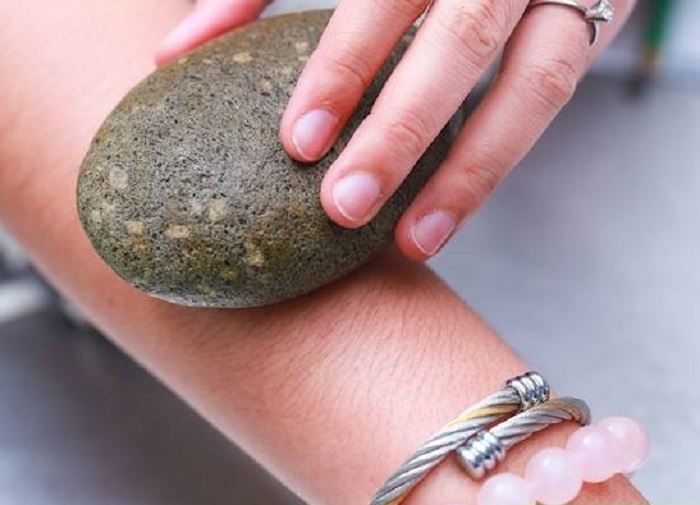

The wide range of use for pumice rock in various areas of construction and medicine has made it one of the best choices of any individual around the globe
The high porosity level causes it to be a best choice to remove dead skin
Also its usage in agriculture as a mineral fertilizer and the power to resist water penetration with decorative use all cause it to be exclusive amongst all its other counterparts
My company is gently honored to have pioneered in supply and export of pumice rock and powder to all countries around the globe at best and most reasonable price
A link is gently provided above for any individual interested in wide variety of our products for browse or purchase online
All you need is just press the link and join us in the world of pumice trade